eBPF Talk: 再论高性能 eBPF ACL 中的 ACL 规则匹配算法比较复杂,晦涩难懂;相对于 iptables 而言,该实现就比较难维护了。这就是为了性能而牺牲了可维护性。
所以,有没有类似 iptables 遍历匹配规则的可维护性高的 eBPF ACL 的实现呢?
有,在 eBPF 里可以使用 bpf_for_each_map_elem() 遍历匹配规则。
源代码: iptables in bpf
bpf_for_each_map_elem()
eBPF helpers 中有遍历 bpf map 的帮助函数, bpf_for_each_map_elem()。当用来遍历 bpf map 时,不就可以用来遍历 ACL 规则了;从而就可以一条一条地匹配 ACL 规则了。
该帮助函数要求 5.13 及以上的内核才支持(BPF Features by Linux Kernel Version)。
该帮助函数的目标场景之一就是防火墙。
该帮助函数的函数签名及使用说明如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
/*
* bpf_for_each_map_elem
*
* For each element in **map**, call **callback_fn** function with
* **map**, **callback_ctx** and other map-specific parameters.
* The **callback_fn** should be a static function and
* the **callback_ctx** should be a pointer to the stack.
* The **flags** is used to control certain aspects of the helper.
* Currently, the **flags** must be 0.
*
* The following are a list of supported map types and their
* respective expected callback signatures:
*
* BPF_MAP_TYPE_HASH, BPF_MAP_TYPE_PERCPU_HASH,
* BPF_MAP_TYPE_LRU_HASH, BPF_MAP_TYPE_LRU_PERCPU_HASH,
* BPF_MAP_TYPE_ARRAY, BPF_MAP_TYPE_PERCPU_ARRAY
*
* long (\*callback_fn)(struct bpf_map \*map, const void \*key, void \*value, void \*ctx);
*
* For per_cpu maps, the map_value is the value on the cpu where the
* bpf_prog is running.
*
* If **callback_fn** return 0, the helper will continue to the next
* element. If return value is 1, the helper will skip the rest of
* elements and return. Other return values are not used now.
*
*
* Returns
* The number of traversed map elements for success, **-EINVAL** for
* invalid **flags**.
*/
static long (*bpf_for_each_map_elem)(void *map, void *callback_fn, void *callback_ctx, __u64 flags) = (void *) 164;
|
注:网络上搜索到的 man 7 bpf-helpers 里不一定有该帮助函数,可以根据内核版本去查看内核源代码里的 include/uapi/linux/bpf.h 头文件;该头文件里就包含了内核所支持的所有 bpf 帮助函数的函数列表,以及函数的使用说明。
遍历匹配 ACL 规则
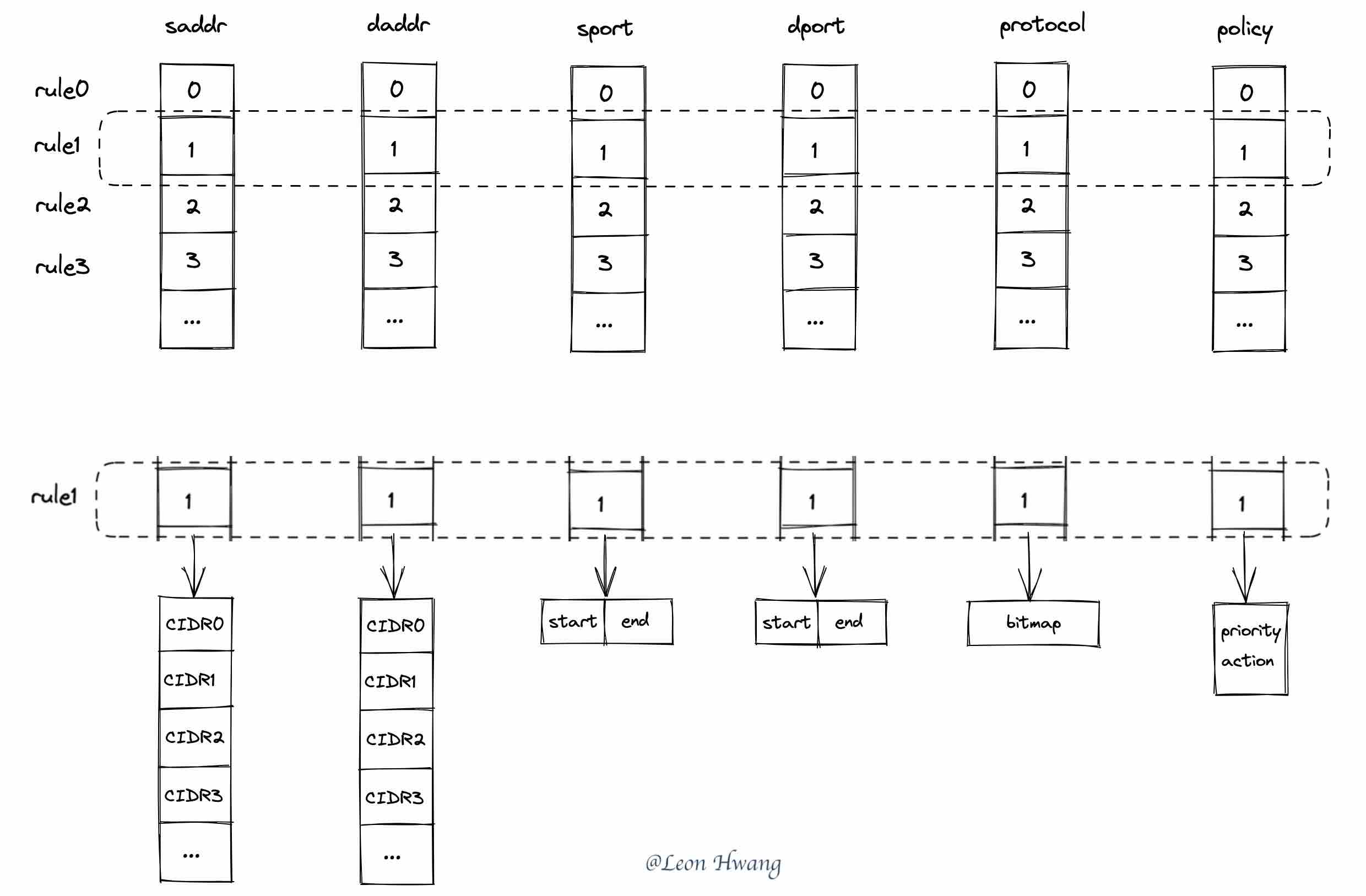
如上图,使用 6 个数组类型的 bpf map 保存 ACL 规则。每条 ACL 规则的五元组以及规则动作使用同一个数组索引保存到那 6 个 bpf map 中。
在 bpf_for_each_map_elem() 遍历其中一个 bpf map 的时候,就可以拿着遍历中的 key (数组索引)去查询另外 5 个 bpf map。
简化代码后的 bpf_for_each_map_elem() 的用法如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
static int
matching_rule(struct bpf_map *map, const __u32 *key, struct rule_policy *value, struct rule_matching *match) {
if (*key >= ACL_RULE_NUM)
return 1;
// protocol
proto = (typeof(proto))bpf_map_lookup_elem(&acl_protocol, key);
// sport
pr = (typeof(pr))bpf_map_lookup_elem(&acl_sport, key);
// dport
pr = (typeof(pr))bpf_map_lookup_elem(&acl_dport, key);
// saddr
m = (typeof(m))bpf_map_lookup_elem(&acl_saddr, key);
val = (typeof(val))bpf_map_lookup_elem(m, &k);
// daddr
m = (typeof(m))bpf_map_lookup_elem(&acl_daddr, key);
val = (typeof(val))bpf_map_lookup_elem(m, &k);
__builtin_memcpy(&match->policy, value, sizeof(*value));
match->matched = 1;
return 1;
}
static __always_inline int
match_acl_rules(struct xdp_md *ctx) {
struct rule_matching match = {};
bpf_for_each_map_elem(&acl_rule_policy, matching_rule, &match, 0);
if (match.matched == 0)
return XDP_PASS;
return match.policy.action;
}
|
详细代码请查看 github.com/Asphaltt/iptables-in-bpf。
iptables VS iptables in bpf
相比于 iptables 每次增删规则时都刷一遍规则,iptables in bpf 里的实现能够做到无损更新规则。
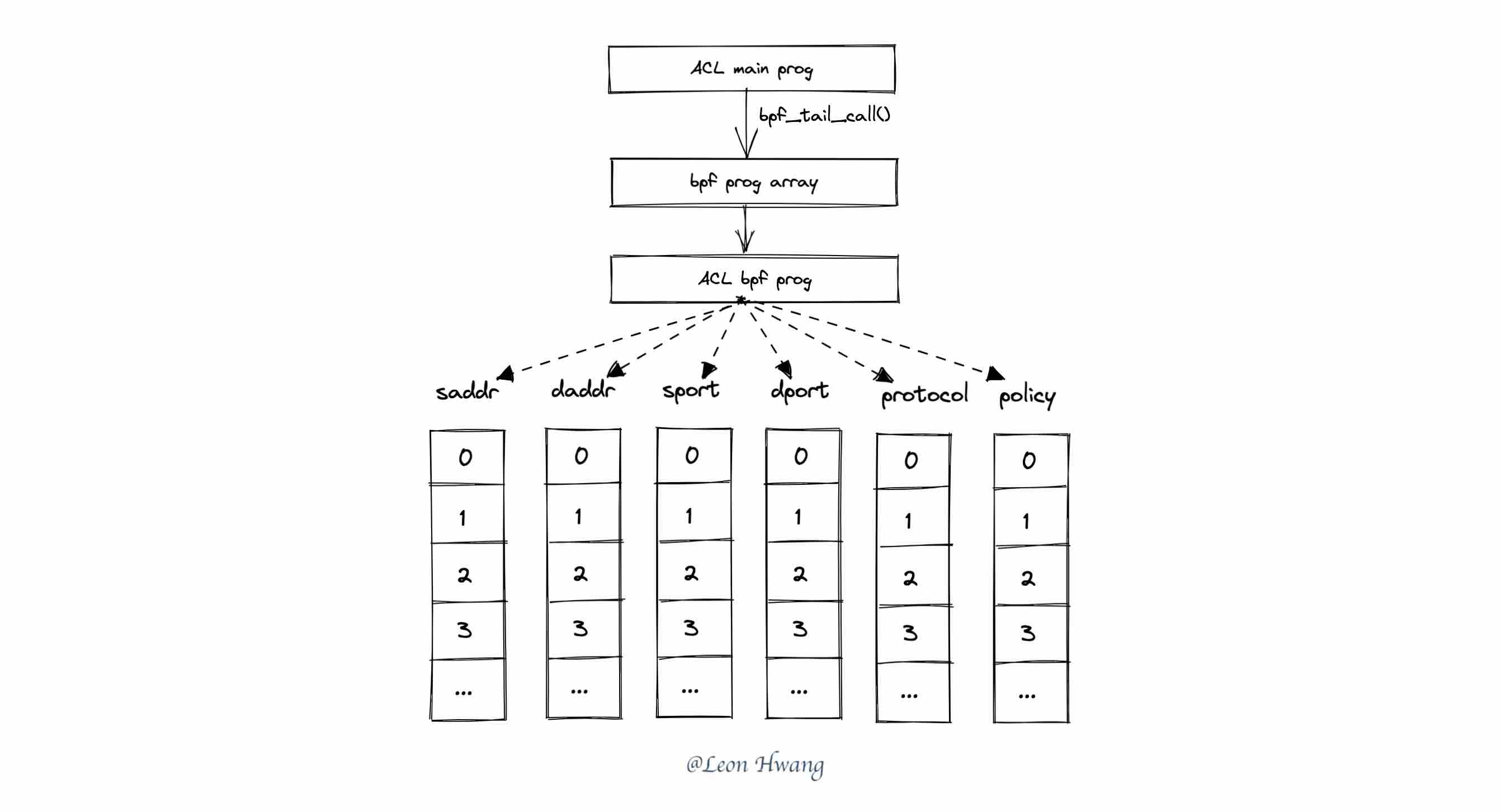
如上图,每次增删规则时,为所有规则使用一份全新的 bpf map 和 ACL bpf prog;将规则数据保存到 bpf map 后,将新的 ACL bpf prog 更新到那个 bpf prog 数组的 bpf map 中。而在 XDP 程序的入口里,直接 bpf_tail_call() 跳到 ACL bpf prog 即可;如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
struct {
__uint(type, BPF_MAP_TYPE_PROG_ARRAY);
__type(key, __u32);
__type(value, __u32);
__uint(max_entries, 1);
} acl_progs SEC(".maps");
SEC("xdp_acl")
int xdp_acl_func(struct xdp_md *ctx) {
bpf_tail_call_static(ctx, &acl_progs, 0);
return XDP_PASS;
}
|
小结
纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行。
即使是 bpf_for_each_map_elem() 看似简单的帮助函数,只有实践起来才知道:为什么 callback_ctx 要指向 bpf 程序运行时所在的栈空间。



