奇葩场景遇到个奇葩问题。
为了更好的性能,就将 XDP 程序挂载到网卡驱动里。但有个业务需求,在 XDP 程序里将需要延迟的流量转发到 veth 设备。所以,就直接在 XDP 程序里将匹配到的流量 bpf_redirect() 到 veth 设备。
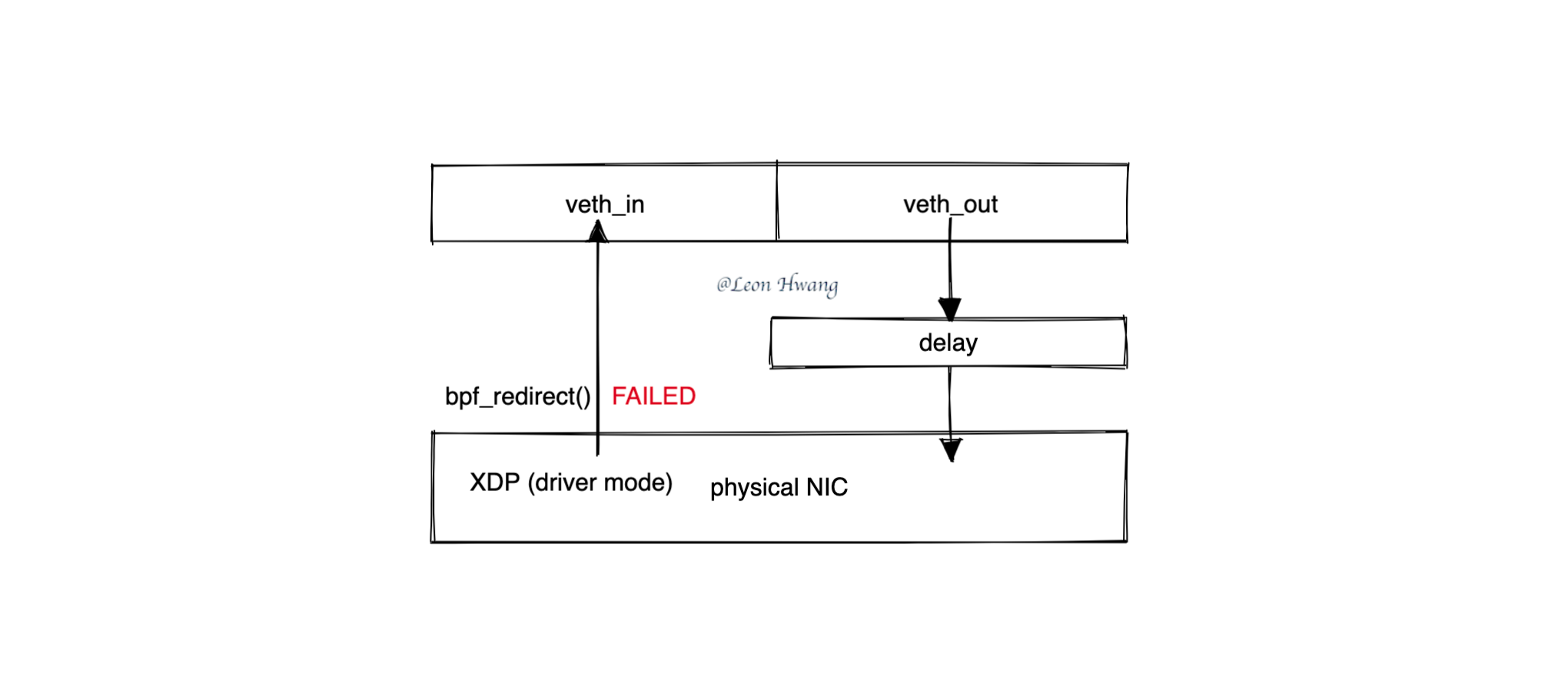
问题就出现在 bpf_redirect() 这里:它转发失败了。
而且,如果该 XDP 程序使用 generic 模式去挂载,它就会转发成功。
问题症状
直接在内核源代码的网卡驱动目录下搜索 BPF_REDIRECT 后,发现网卡驱动转发网络包时的函数调用栈:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
xdp_do_redirect() // ${KERNEL}/net/core/filter.c
|-->dev_xdp_enqueue() // ${KERNEL}/kernel/bpf/devmap.c
|-->__xdp_enqueue()
|-->xdp_ok_fwd_dev()
|-->bq_enqueue()
|-->bq_xmit_all()
|-->dev->netdev_ops->ndo_xdp_xmit()
// => veth_ndo_xdp_xmit() // ${KERNEL}/drivers/net/veth.c
|
对于目标设备类型是 veth 的情况,最终会调用目标设备的 ndo_xdp_xmit() 函数进行发包,即 veth_ndo_xdp_xmit() 函数。
直接 trace 一下 veth_ndo_xdp_xmit() 函数的返回结果吧。
使用一下 bpftrace 脚本进行 trace。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
#!/usr/bin/env bpftrace
#include <linux/netdevice.h>
kprobe:veth_ndo_xdp_xmit
{
$dev = (struct net_device *)arg0;
$flags = arg3;
printf("sizeof netdev: %d\n", sizeof(struct net_device));
printf("veth xdp xmit on %d:%s flags:%d\n", $dev->ifindex, $dev->name, $flags);
@xdpxmit[tid] = $dev->ifindex;
}
kretprobe:veth_ndo_xdp_xmit
/@xdpxmit[tid]/
{
$ifindex = @xdpxmit[tid];
delete(@xdpxmit[tid]);
printf("veth xdp xmit on %d return %d\n", $ifindex, retval);
}
END
{
clear(@xdpxmit);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
# bpftrace veth_ndo_xdp_xmit.bt
Attaching 3 probes...
sizeof netdev: 2432
veth xdp xmit on 84:veth_xxx0 flags:1
veth xdp xmit on 84 return -6
|
veth_ndo_xdp_xmit() 返回的 -6 是什么情况?
1
2
|
# errno -l | grep 6
ENXIO 6 No such device or address
|
明明有目标设备,为什么会是 No such device or address 呢?
接着撸下 veth_ndo_xdp_xmit() 的源代码吧。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
// ${KERNEL}/drivers/net/veth.c
veth_ndo_xdp_xmit()
|-->veth_xdp_xmit() {
struct veth_priv *rcv_priv, *priv = netdev_priv(dev);
int ret = -ENXIO;
rcv = rcu_dereference(priv->peer);
if (unlikely(!rcv))
goto out;
rcv_priv = netdev_priv(rcv);
rq = &rcv_priv->rq[veth_select_rxq(rcv)];
/* The napi pointer is set if NAPI is enabled, which ensures that
* xdp_ring is initialized on receive side and the peer device is up.
*/
if (!rcu_access_pointer(rq->napi))
goto out;
out:
return ret;
}
|
如此看来,要么是没有 peer 设备,要么是没有开启 NAPI。
尽管说 veth 设备一定会有 peer 设备,还是确认一下吧。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
|
#!/usr/bin/env bpftrace
#include <linux/netdevice.h>
struct veth_rq {
struct napi_struct xdp_napi;
struct napi_struct *napi; /* points to xdp_napi when the latter is initialized */
struct net_device *dev;
void *xdp_prog;
};
struct veth_priv {
struct net_device *peer;
void *dropped;
void *xdp_prog;
struct veth_rq *rq;
unsigned int requested_headroom;
};
kprobe:veth_ndo_xdp_xmit
{
$dev = (struct net_device *)arg0;
$flags = arg3;
printf("sizeof netdev: %d\n", sizeof(struct net_device));
printf("veth xdp xmit on %d:%s flags:%d\n", $dev->ifindex, $dev->name, $flags);
$priv = (struct veth_priv *)((uint8 *)$dev + sizeof(struct net_device));
$rcv = (struct net_device *)$priv->peer;
if ($rcv != 0) {
printf("veth rcv netdev is %d:%s\n", $rcv->ifindex, $rcv->name);
$rcv_priv = (struct veth_priv *)((uint8 *)$rcv + sizeof(struct net_device));
$rq = (struct veth_rq *)$rcv_priv->rq;
if ($rq != 0) {
printf("veth rcv netdev is %d:%s with rq\n", $rcv->ifindex, $rcv->name);
$napi = (struct napi_struct *)$rq->napi;
if ($napi != 0) {
printf("veth rcv netdev is %d:%s with rq with napi\n", $rcv->ifindex, $rcv->name);
} else {
printf("veth rcv netdev is %d:%s with rq without napi\n", $rcv->ifindex, $rcv->name);
}
} else {
printf("veth rcv netdev is %d:%s without rq\n", $rcv->ifindex, $rcv->name);
}
}
@xdpxmit[tid] = $dev->ifindex;
}
kretprobe:veth_ndo_xdp_xmit
/@xdpxmit[tid]/
{
$ifindex = @xdpxmit[tid];
delete(@xdpxmit[tid]);
printf("veth xdp xmit on %d return %d\n", $ifindex, retval);
}
END
{
clear(@xdpxmit);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
# bpftrace veth_ndo_xdp_xmit.bt
Attaching 3 probes...
sizeof netdev: 2432
veth xdp xmit on 84:veth_xxx0 flags:1
veth rcv netdev is 85:veth_yyy0
veth rcv netdev is 85:veth_yyy0 with rq
veth rcv netdev is 85:veth_yyy0 with rq without napi
veth xdp xmit on 84 return -6
|
至此可知,是 peer 设备上没有开启 NAPI。
问题解决
所以,该如何给 veth 设备开启 NAPI 呢?
直接问 Google 和 ChatGPT 无果,还是直接撸 veth 的源代码吧;整个 veth.c 文件也就不到 2000 行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
static int veth_set_features(struct net_device *dev,
netdev_features_t features)
{
netdev_features_t changed = features ^ dev->features;
struct veth_priv *priv = netdev_priv(dev);
int err;
if (!(changed & NETIF_F_GRO) || !(dev->flags & IFF_UP) || priv->_xdp_prog)
return 0;
if (features & NETIF_F_GRO) {
err = veth_napi_enable(dev);
if (err)
return err;
} else {
veth_napi_del(dev);
}
return 0;
}
|
当看到这个函数时,便可知要开启 NAPI,只需要开启设备的 GRO 功能即可。所需命令行如下:
1
|
ethtool -K veth_yyy0 gro on
|
或许这行命令只值 1 块钱,但这行命令背后所需要的知识就值 999 块钱。
当开启 GRO 时,bpf_redirect() 转发成功;当关闭 GRO 时,bpf_redirect() 转发失败。
那么问题来了:为什么一定要开启 GRO 呢?且听下回分解。
小结
强撸灰飞烟灭。
遇到奇葩问题,还是得强撸内核源代码。


